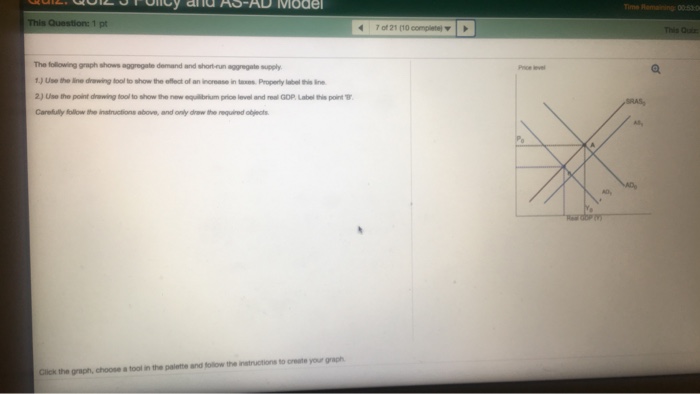
The Following Graph Shows Aggregate Demand and Short-run Aggregate Supply
Machines factories and buildings demanded by firms and households. The price level and the quantity of capital goods.
Solved The Following Graph Shows Aggregate Demand And Chegg Com
The following graph shows the short-run aggregate supply curve AS the aggregate demand curve AD and the long-run aggregate supply curve LRAS for a hypothetical economy.
. Distinguish between the short run and the long run as these terms are used in macroeconomics. 1 1 The economy is in an expansion with low unemployment and high output. Aggregate supply refers to the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply.
At point A the price level is 140 and the quantity of output demanded is 300 billion. Nominal nominal real the classical dichotomy. Module 5 quiz 2.
Initially the expected price level is equal to the actual price level and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at its natural rate of output 100 billion. The following graph shows the short-run aggregate-supply curve AS the aggregate-demand curve AD and the long run aggregate-supply curve LRAS for a hypothetical economy. The economy is in.
The short run aggregate supply curve shows the relationship in the short run between a. The Short-Run Curve. The SRAS curve is also drawn to reflect some variables such as the nominal wage rate.
Initially the expected price level is equal to the actual price level and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at its natural level of output 80 billion. Economists use the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply to examine the economys short-run fluctuations around the long-run output level. According to the graph the aggregate demand curve meets the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left of the long-run aggregate supply.
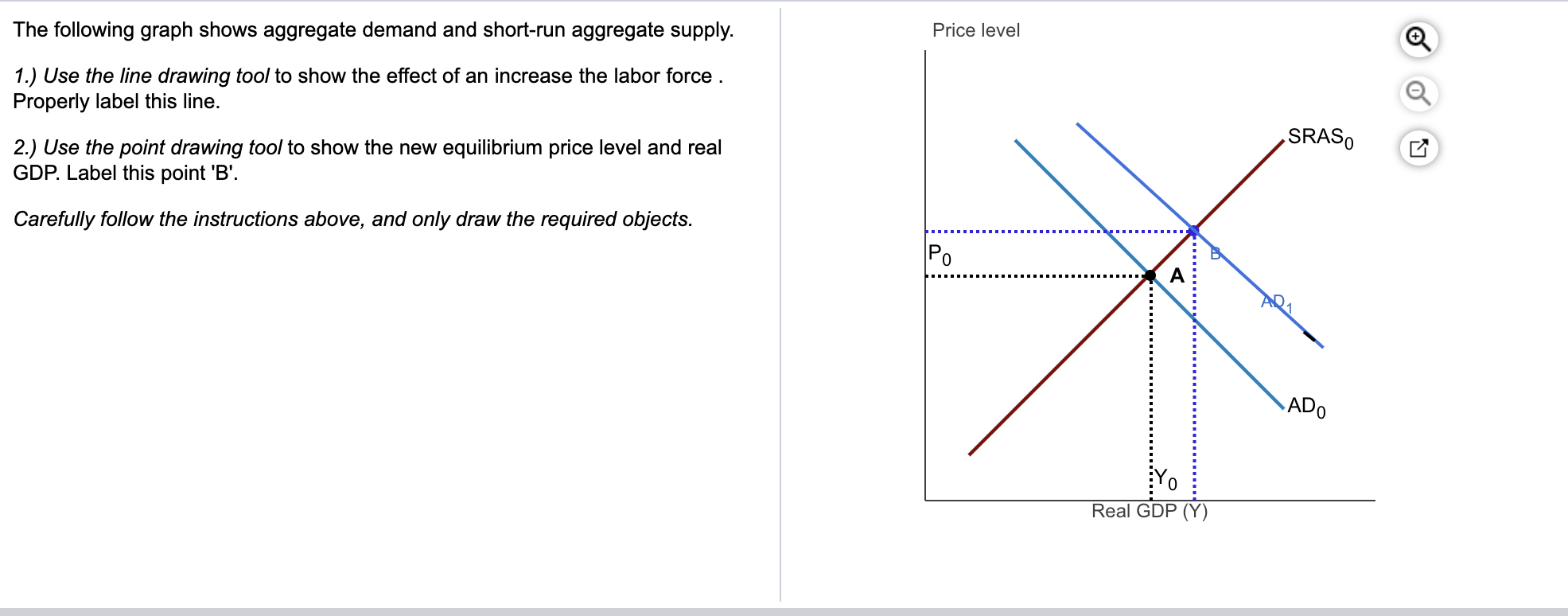
Label this point B. Initially the expected price level is equal to the actual price level and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at its LRAS of 80 billion. SRASO 2 Use the point drawing tool to show the new equilibrium price level and real GDP.
Short-run equilibrium and long-run aggregate supply The following graph shows several aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves for an economy whose potential output is 5 trillion. The following graph shows the short-run aggregate supply curve As the aggregate demand curve AD and the long-run aggregate supply curve LRAS for a hypothetical economy. Properly label this line.
To return the economy to the natural rate of output the Fed could. Moving down along the aggregate demand curve from point A to point B the price level falls to 120 and the quantity of output demanded. The graph above shows aggregate demand AD short-run aggregate supply SRAS and long-run aggregate supply curves for an economy.
This means it goes upward sloping rather than full vertical. Initially the expected price level is equal to the actual price level and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at its natural level of output 110 billion. The following graph shows the long-run aggregate-supply curve LRAS the short-run aggregate-supply curve AS and the aggregate-demand curve for an economy.
In the short run however most economists believe that real and nominal variables are intertwined. Initially the expected price level is equal to the actual price level and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at its natural level of output 110 billion. In the short run the aggregate supply curve reacts to the price level.
The following graph shows the short-run aggregate supply curve ASAS the aggregate demand curve ADAD and the long-run aggregate supply curve LRASLRAS for a hypothetical economy. With unemployment and. Draw a hypothetical long-run aggregate supply curve and explain what it shows about the natural levels of employment and output at various price levels given changes in aggregate demand.
Initially the expected price level is equal to the actual price level and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at its natural level of output 100 billion. The following graph shows the short-run aggregate supply curve AS the aggregate demand curve AD and the long-run aggregate supply curve LRAS for a hypothetical economy. The following graph shows the long-run aggregate-supply curve LRAS the short-run aggregate-supply curve AS and the aggregate-demand curve for an economy.
The following graph shows the short-run aggregate supply curve AS the aggregate demand curve AD and the long-run aggregate supply curve LRAS for a hypothetical economy. The following graph shows aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply Price level 1 Use the line drawing tool to show the effect of an adjustment of workers and firms to a higher than expected price level. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run.
This is a recessionary situation and indicates that the actual production or output is. Among the factors held constant in drawing a short-run aggregate supply curve are the capital stock the stock of natural resources the level of technology and the prices of factors of production. Initially the expected price level is equal to the actual price level and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at its natural level of output 120 billion.
A curve that shows the relationship in. Why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward The following graph shows the aggregate demand AD curve in a hypothetical economy. The following graph shows the short-run aggregate supply curve AS the aggregate demand curve AD and the long-run aggregate supply curve LRAS for a hypothetical economy.
So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve. The following graph shows the short-run aggregate supply curve the aggregate demand curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve for a hypothetical economy. Initially the expected price level is equal to the actual price level and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at its natural level of output 110 billion.
Long-run aggregate supply curve. The short-run aggregate supply SRAS curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between production and the price level in the short run. The following graph shows an incomplete short-run aggregate demand AD.
The price level and the quantity of real GDP demanded by firms b. The curves are labelled a b c and d. Based on the graph cost-push inflation is caused by a movement from A SRAS1SRAS1 to SRAS2SRAS2 B SRAS2SRAS2 to SRAS1SRAS1 C AD1AD1 to AD2AD2 D AD2AD2 to AD1AD1 E Y1Y1 to Yf.
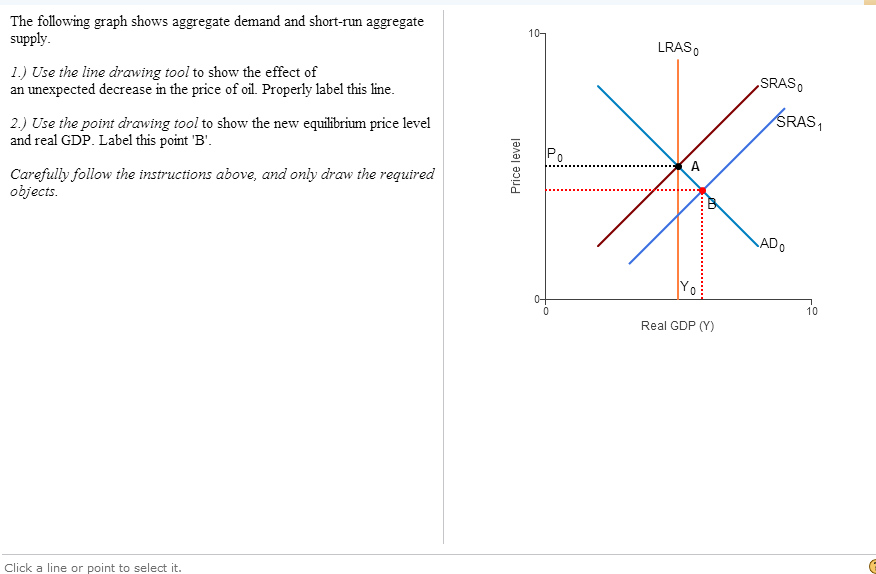
Solved The Following Graph Shows Aggregate Demand And Chegg Com

Solved The Following Graph Shows Aggregate Demand And Chegg Com

Solved The Following Graph Shows Aggregate Demand And Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment